by Aspirant Team
April 17, 2023
Business analytics is the practice of using data and analytical techniques to gain insights that help inform business decisions. With the right approach, organizations can unlock a wealth of valuable information from the data they are already generating to make faster, more informed strategic choices. It has become an essential tool for business leaders as they seek opportunities for growth and a competitive edge for their companies.
This refers to a complex process that involves gathering, analyzing and interpreting data to drive decision-making. It is a multidimensional approach to data analysis that encompasses business intelligence, data mining, and predictive modeling techniques. With the help of advanced analytical tools, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and outliers that hold the key to solving their toughest challenges.
Through proper analysis, companies can find patterns, relationships and trends that enable them to make faster, better decisions in their operations. The ability to spot trends and react quickly creates 'strategic agility' that can provide a competitive advantage.
Decision-making becomes much faster and far less subjective when using a defined, consistent approach for reacting to objective inputs (various data sets). This mitigates the substantial risk that comes with leading companies by intuition alone.
Business intelligence (BI) is about understanding what happened in the past. Companies can see how they did in the past and use that information to plan for the future.
Data analytics is a general term that refers to the concept of leveraging data to make better decisions.
Data analysis is a subset of data analytics where specific processes define how data is inspected, processed, and interpreted. More sophisticated approaches apply statistical and computational techniques as well as machine learning in order to handle larger data sets, accelerate its analysis, and represent it visually.
These programs encompass a series of processes that translate raw data into insight. Business data from a variety of internal and external sources is aggregated, analyzed, and presented in a format that allows decision makers to quickly understand it. They can then collaborate and align on the corresponding course of action in very short order.
Direct integration of the data feeds and dashboards can accelerate these efforts to the point where data driven decision making is nearly automatic.
The potential uses are only limited by the scope and volume of available data. With the right inputs, analysis can uncover actionable insights within customer behavior, market trends, sales performance, or operational efficiency. Companies of any size or industry stand to gain a material advantage by developing an effective data analytics strategy.
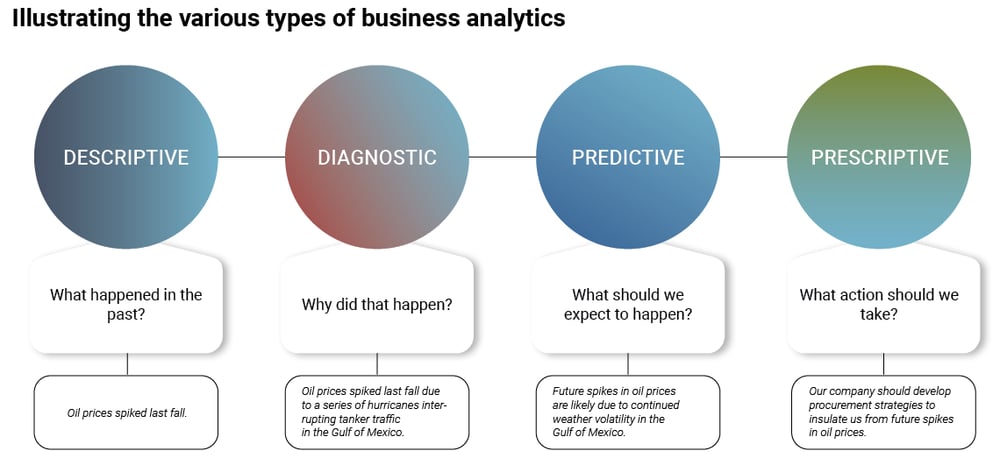
Descriptive analytics uses historical business data to describe what happened in the past.
Diagnostic analytics, or 'drill-down analytics', is used to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations in historical data that explain why something happened.
Predictive analytics identifies patterns in data to predict future outcomes. Methods such as regression analysis, decision trees, neural networks, and clustering can help establish and quantify the cause-and-effect relationships between any number of business dynamics.
Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending what should be done in a given situation to achieve a desired outcome. Mathematical modeling, simulation, machine learning, and optimization are often part of these frameworks.
Spreadsheet software such as Microsoft Excel is the typical starting point for basic data analytics. However, most companies quickly opt for more powerful data analytics tools that are capable of more robust and faster analysis.
Through systems integrations and the development of custom applications, companies can virtually eliminate the time, effort, and potential for errors inherent with manual data management.
Microsoft's Power BI is one of the most popular solutions for data visualization. It provides dynamic dashboards that empowers users to see and dig into data in real time. They can be customized and configured to show the most important metrics in the most intuitive way.
In addition to software and systems, organizations need business analysts with a broad set of skills in order to conduct analysis properly:
Enabling analytical capabilities requires a systematic approach that involves the integration of technology, data management, and human expertise. Companies need to invest in the right resources and infrastructure to support continuous improvement and innovation.
Here are some critical steps that companies can take to develop these capabilities internally:
It is easy to get excited about the potential impact of leveraging data to fuel business growth, but there tend to be some challenges in standing up these programs.
Here are some of the hurdles that companies tend to encounter:
Leaders are willing to face these challenges because they realize the potential upside of revolutionizing how their companies run. Few have the time, resources, and expertise to do that on their own and avoid all the pitfalls along the way. That's where we come in.
Aspirant's data and analytics experts know how to anticipate, identify, and resolve problems that would otherwise limit data analytics programs or prevent them from ever being implemented.
We can also develop custom applications and/or integrations to install a comprehensive data collection infrastructure.
As mentioned above, there is much more to cultivating analytical capabilities than technology. Aspirant's delivery model is based on Integrated Expertise, which provides direct access to all the cross-functional support needed to stand up a state-of-the-art, difference-making business intelligence program.